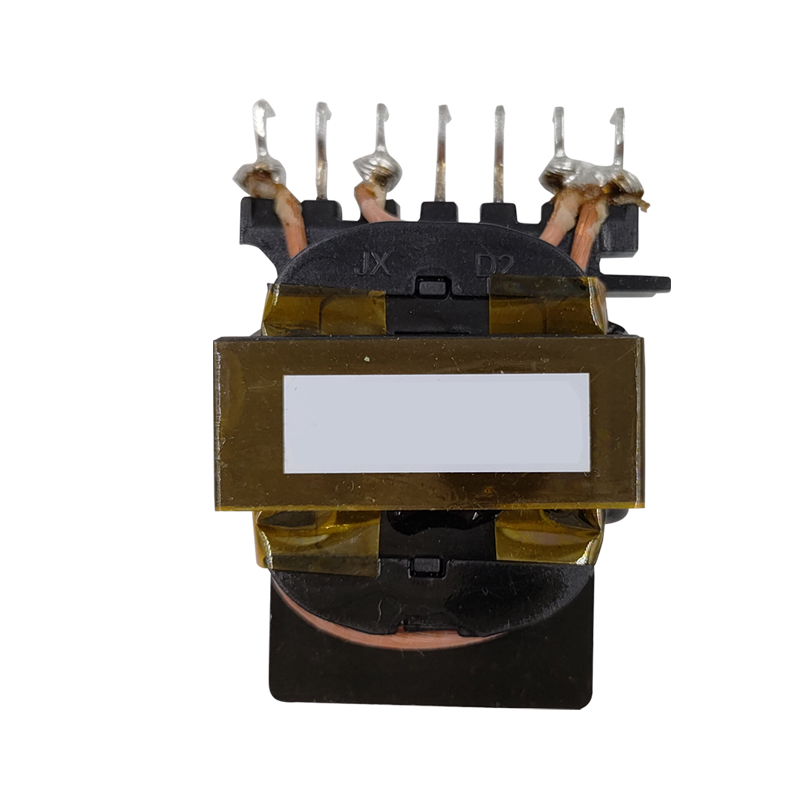
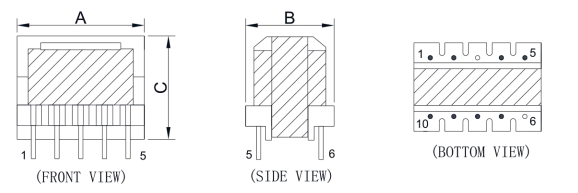
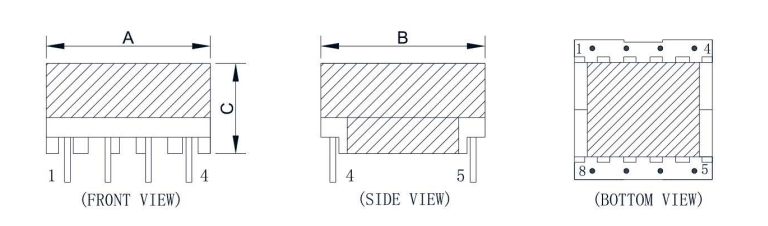
What is the difference between a flyback transformer and a normal transformer?
2024-04-27
Flyback transformers and normal transformers differ in their design, operation, and applications. Here are the key differences between the two:
- Operation:
- Normal Transformer: A normal transformer operates continuously in a steady-state manner, with energy transferred from the primary winding to the secondary winding as alternating current (AC) flows through the windings.
- Flyback Transformer: A flyback transformer operates in a discontinuous manner, storing energy in its magnetic core during the "on" period of the input signal and releasing it to the load during the "off" period. This discontinuous operation allows for voltage step-up or step-down, isolation, and energy storage.
- Primary Winding:
- Normal Transformer: A normal transformer typically has a primary winding and a secondary winding, with a fixed turns ratio between them.
- Flyback Transformer: A flyback transformer also has a primary winding and a secondary winding, but it may have additional windings for energy storage and feedback purposes. The turns ratio of a flyback transformer can be varied to achieve different voltage outputs.
- Core Design:
- Normal Transformer: Normal transformers often use a laminated iron or ferrite core to guide and concentrate the magnetic flux.
- Flyback Transformer: Flyback transformers may use similar core materials, but they are designed to operate in a different mode, with energy stored in the core during one portion of the cycle and released during another.
- Applications:
- Normal Transformer: Normal transformers are commonly used for voltage conversion, impedance matching, and isolation in various electronic devices and power distribution systems.
- Flyback Transformer: Flyback transformers are commonly used in applications requiring high-voltage isolation, voltage step-up or step-down, such as CRT displays, high-voltage power supplies, DC-DC converters, and certain types of inverters.
- Energy Storage:
- Normal Transformer: In a normal transformer, energy transfer occurs continuously from the primary to the secondary winding without significant energy storage.
- Flyback Transformer: Flyback transformers store energy in the magnetic core during the "on" period of the input signal and release it to the load during the "off" period, allowing for energy storage and voltage conversion.
Overall, while both normal transformers and flyback transformers are used for voltage transformation and isolation, their operating principles, designs, and applications differ significantly. Flyback transformers are specifically designed for applications requiring energy storage and discontinuous operation, while normal transformers operate continuously in a steady-state manner.